-

-
Type 1 Diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and was previously known as juvenile diabetes. Only 5% of people with diabetes have this form of the disease.
-
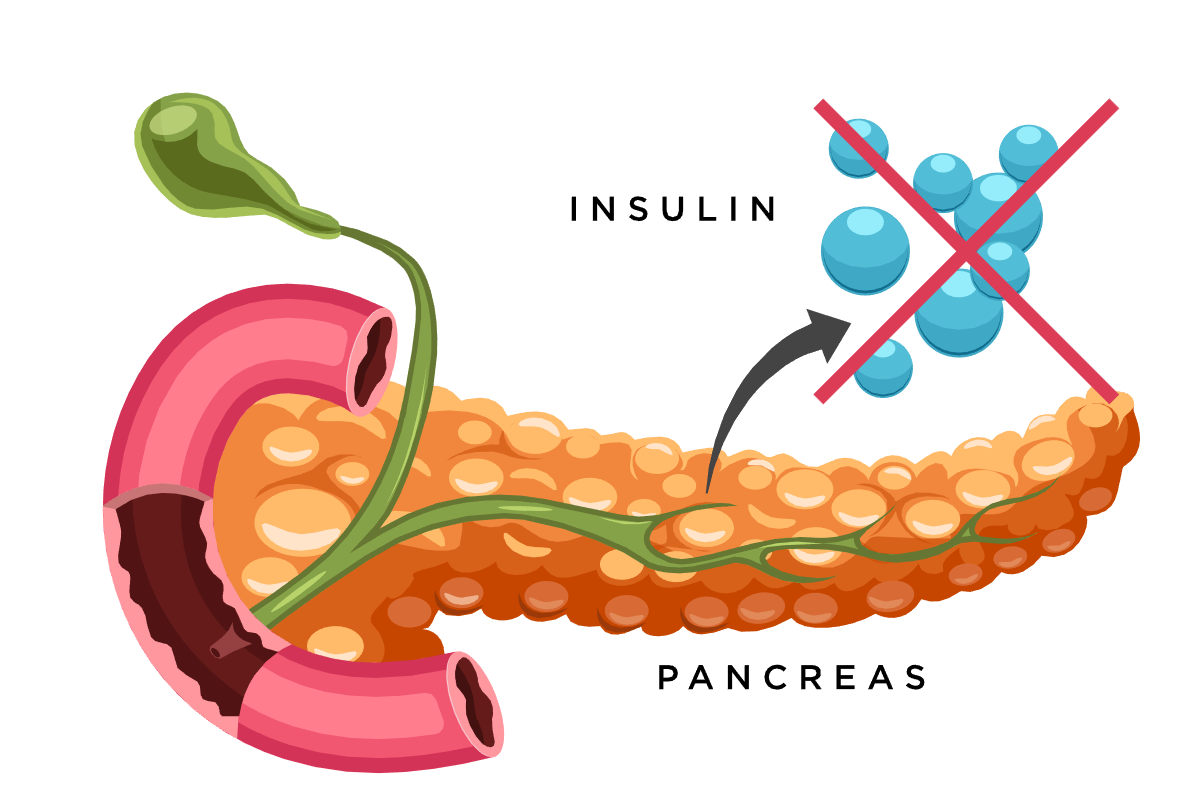
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Treatment focuses on managing blood sugar levels with insulin, diet, and lifestyle changes.
-
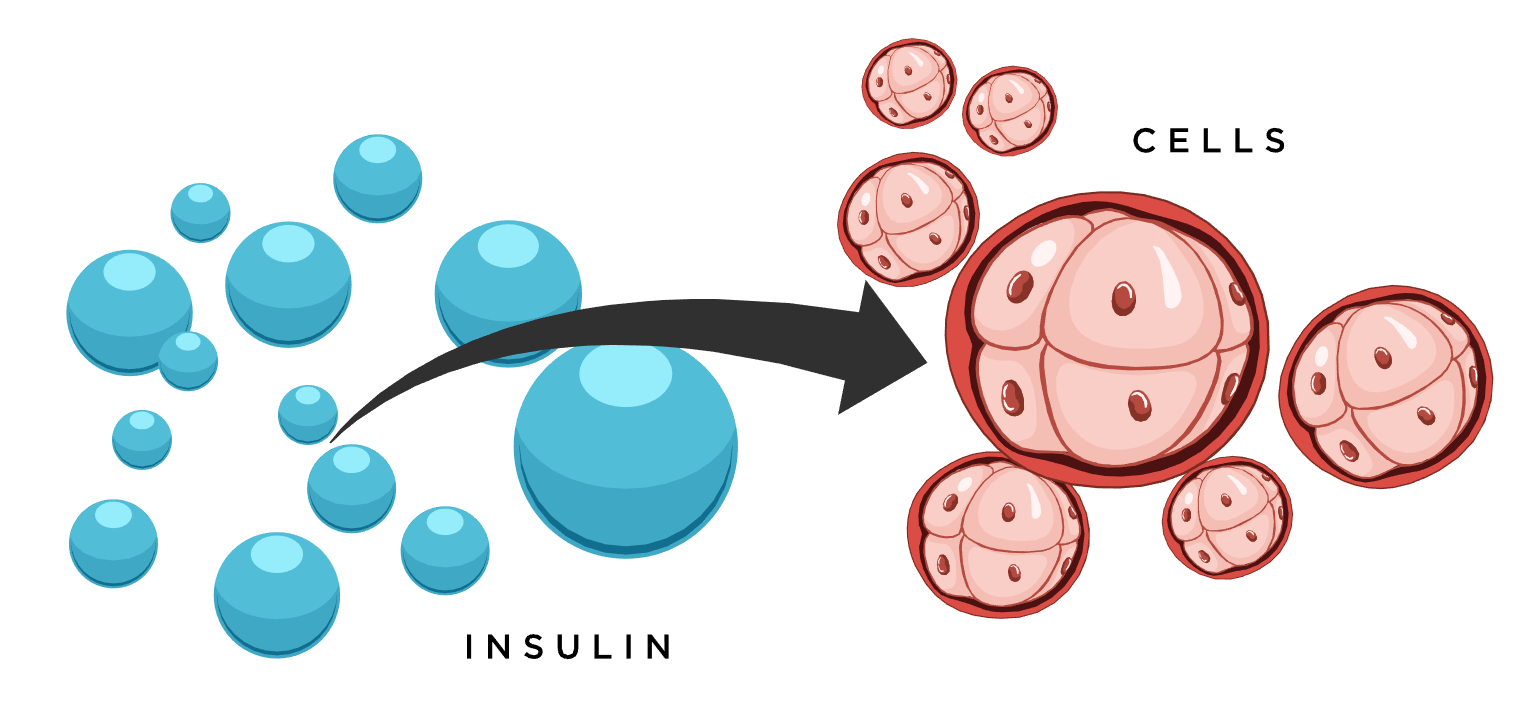
Insulin is a hormone that the body needs to get glucose from the bloodstream into the cells of the body.
-
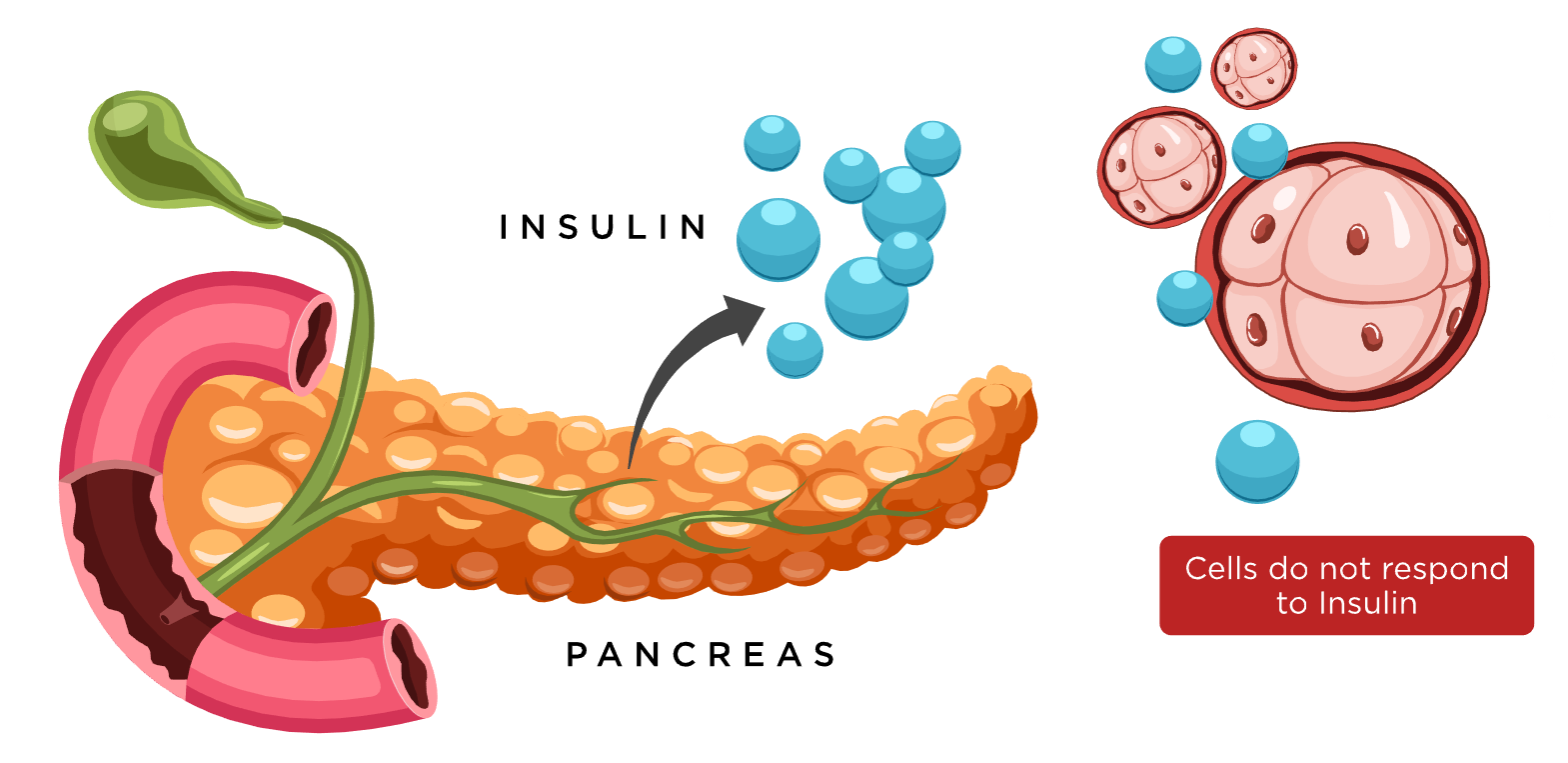
In type 2 diabetes, your cells respond poorly to insulin and take in less sugar, a condition known as “insulin resistance.” This can lead to hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar levels.
-
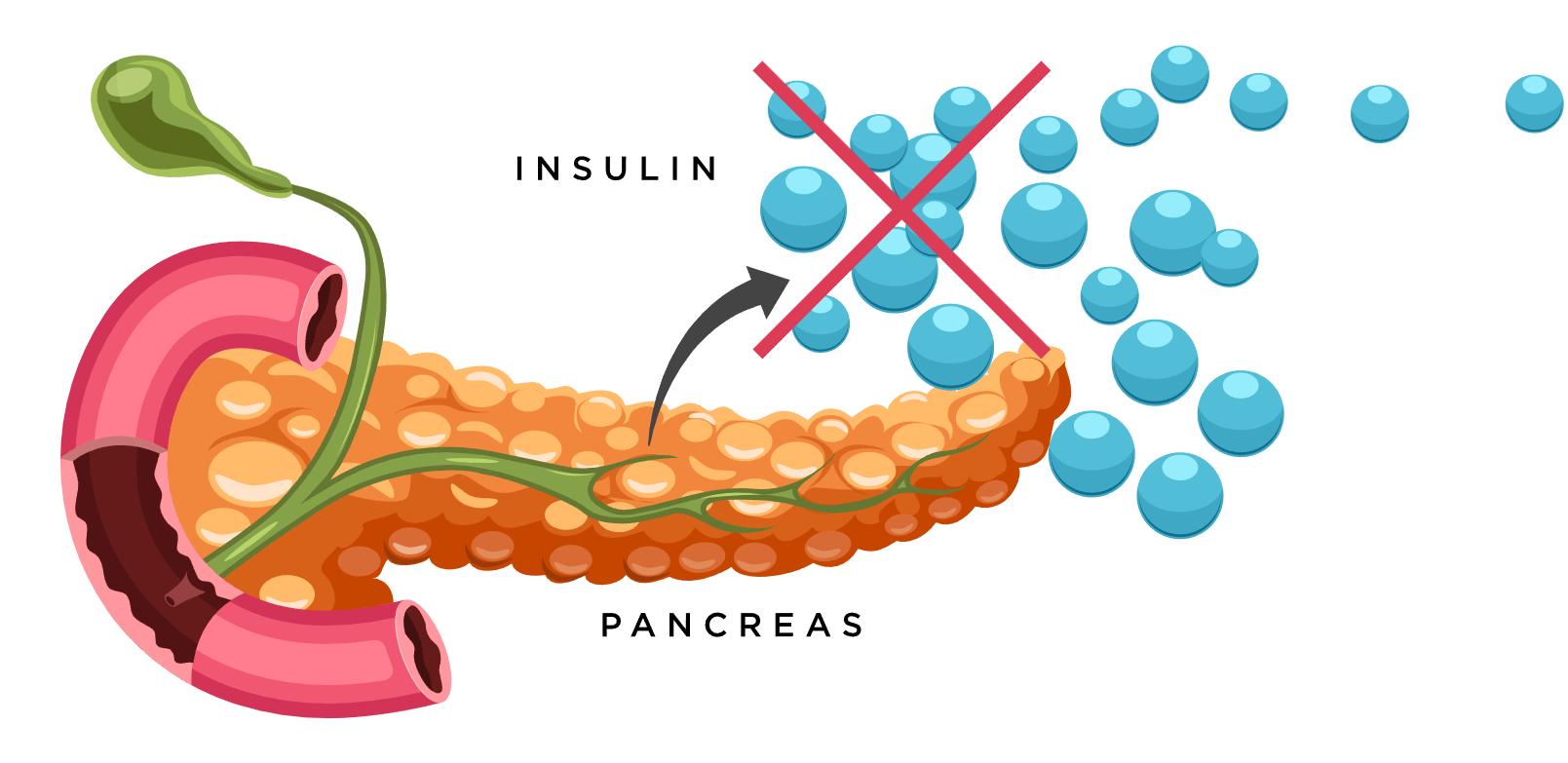
If hyperglycemia is not properly managed, it can lead to complications, such as heart disease and stroke, blindness, kidney disease, and nerve damage.